Ureteric Stents
What is a ureteric stent?
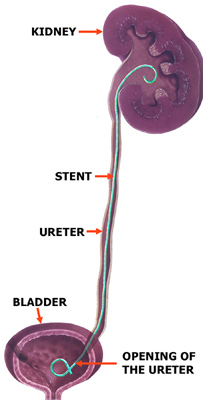
A ureteric stent is a specially designed hollow tube, made of a flexible plastic material that is placed in the ureter. The length of the stents used in patients varies from 24 to 30 cm.
Why is a Ureteric stent used?
Generally, a ureteric stent is used to relieve or prevent obstruction of the kidney. The obstruction causes pressure to build up which can be very painful. The function of the kidney can also suffer which can lead to infection and further damage to the kidneys.
The stent is used
- To relieve the obstruction on a temporary basis before treatment or an operation is carried out.
- Following an operation on the ureters, as it takes time for the ureters to heal and a temporary measure to prevent obstruction
Dr Vass will provide further details applicable to you.
How does a stent stay in place?
The stents are designed to stay in the urinary system by having both the ends coiled. The top end coils in the kidney and the lower end coils inside the bladder to prevent its displacement.
How is a ureteric stent put in place?
Usually, a stent is placed under a general anaesthetic using a special telescope (cystoscope) which is passed through the urethra into the bladder. The stents are then placed in the ureter and kidney via the opening of the ureter in the bladder.
Occasionally they are placed from the kidney down to the bladder using special X-ray techniques. The correct position of a stent is checked by taking an X-ray.
How long will the stent stay in the body?
There is no set time limit and will be kept in place as long as necessary or until the obstruction is relieved.
In the majority of patients, the stents are only required for a short duration, from a few weeks to 12 months.
Possible side effects associated with a stent.
The majority of patients with a stent in place will be aware of its presence some of the time. In most cases they are minor and tolerable, however sometimes they can be moderate to severe in nature.
Common side effects are:
- Urinary symptoms – which may include:
- An increased frequency of passing urine
- Urgency to pass urine
- Small amount of blood in urine.
- The sensation of incomplete emptying of the bladder
- Occasionally, especially in women, there is a slight risk of incontinence episodes.
- Discomfort or pain
- This may occur commonly in the bladder, kidney area, but sometimes in other areas such as the groin, urethra and genitals.
- Pain or discomfort may be more noticeable after physical activities and during and after passing urine.
- Possibility of a urinary tract infection: Symptoms are:
- Raised temperature
- increased pain or discomfort in the kidney or bladder area
- an increase in other urinary symptoms, such as burning sensation or pain while passing urine
- General feeling of unwell
At home after the Operation
You may relieve some of the side effects by the following care:
- It is essential that you drink at least 1 ½ to 2 litres of fluids, mainly water a day. This will reduce the risk of getting an infection and reduce the amount of blood in the urine.
- If you experience pain or discomfort, take pain relief as prescribed by your doctor. Please note codeine can cause constipation.
- Take ural (urinary alkalisers) 3 times a day, to help relieve the burning sensation while passing urine.
- If you have a stent with a thread coming down from the urethra outside the body, then more care will be needed so as not to dislodge the thread.
Contact Your Surgeon
Contact your surgeon if you have any of these problems after insertion of your stent:
- Constant and unbearable pain associated with the stent.
- Symptoms of a urinary tract infection.
- The stent gets dislodged or falls out
- If you notice a significant change in the amount of blood in your urine.
Living with Ureteric Stent
The stent is not expected to cause much disruption to your normal daily life; however, you may experience some side effects either directly or indirectly in relation to various daily activities.
Physical, sport and work activities
You may carry on with various physical and work activities while the stent is in place provided the underlying kidney condition and your health allows you to do so. Occasionally side effects, such as urinary symptoms and pain associated with the stent can make you feel more tired than normal.
Social Life and Interactions
The presence of the stent should not affect this in a significant way. Due to urinary symptoms such as, increased frequency and urgency, you may need to use toilets more frequently.
Sex
Few patients experience discomfort during sexual activities. Sometimes the side effects associated with the stent may have an effect on the sexual desire. If you have a stent with a thread coming outside the body, sexual activities may be difficult and care will also be required so as not to dislodge the thread.
Please note following General anaesthetic, you must not drive or travel on public transport alone for 24 hours and you must ensure that you have someone to take you home from the hospital. |
